Navigating the aftermath of a data breach can be a confusing and stressful experience. Whether it’s a major company or a small business, a data breach means your personal information might be compromised. So, what should you do? Here’s a guide on how to react and what your options are.
Cybercrime has gotten a lot scarier as the methods have become more sophisticated and difficult to detect. They might look like official business, but in reality, they are dangerous and well-thought-out attacks that can endanger your company and all those who work for it. Today, we want to break down some of the ways these cyberthreats can fool even the most cautious employees.
Every day, cybercriminals wake up and choose violence. Whether it’s a nasty strain of ransomware demanding a king’s ransom or a sneaky little virus that just wants to watch your business burn, the threats never stop coming. That’s why locking down your business is as essential as putting cream in your morning coffee.
Everywhere you look on the Internet, there’s a scam, threat, or other malicious entity. Okay, maybe that’s not 100% true, but the possibilities are nearly endless for hackers. They’ll hide spyware, adware, and even ransomware online, so you must take measures to ensure that your devices and business are safe.
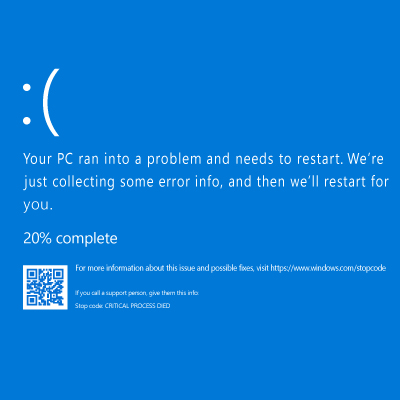
July 18th, 2024 saw one of the most widespread and devastating outages in recent memory, as a global update from cybersecurity company CrowdStrike brought about significant impacts to major infrastructures and societal needs. All this occurred even though only 1% of Windows operating systems experienced the issue.
Every year, there seems to be a notable increase in high-profile ransomware attacks. If you haven’t yet devised a plan to shield your business from these dangers, the time to act is now. Luckily, there are proactive steps you can take to reduce the impact of ransomware attacks, and it all starts with preparation.
Did you know that the first case of ransomware surfaced in 1989? Since then, it has grown far more dangerous and common. Let’s examine some of the numbers regarding ransomware and how you can avoid it affecting your organization.
Ransomware is perhaps the nastiest threat you can encounter, and the unprepared business could potentially be crippled beyond repair if it suffers from an attack like this. We’re here to demystify the inner machinations of a ransomware attack so you know better how to respond to it.
For the most part, Microsoft takes security as seriously as it should, issuing updates and patches to maintain your Windows and Server operating systems. While you can count on receiving these updates for your supported operating systems, what you might not have known is that Microsoft accidentally overlooked a flaw in its own defenses.
Malware has been a problem for people that rely on technology for decades. Like the security that is designed to mitigate the effect of malware, the malware itself has grown in potency and frequency and is a major problem for businesses. Today, we will take a look at a few ways you can get malware.